The Pipe Schedule Number is a standard method used to define the thickness of pipes in process plants.
Standardization of wrought steel pipe schedules and sizes began during the era of mass production. Initially, pipes were available in only three sizes: standard weight (STD), extra strong (XS), and double extra strong (XXS), based on the iron pipe size (IPS) system.
However, as industries modernized and the use of pipes expanded to accommodate various pressure and temperature conditions, these three sizes became insufficient. This led to the development of the schedule number, which incorporates both the wall thickness and diameter of the pipe.
Currently, pipe size is identified by two sets of numbers:
1-Pipe schedule, which indicates the wall thickness of the pipe.
2-Pipe bore/nominal diameter
What is Nominal Pipe Size?
Nominal pipe size (NPS) is a measurement that indicates the size of a pipe. For example, when we refer to a “6-inch pipe,” the “6-inch” denotes its nominal size. For pipe sizes NPS 14 and above, the outside diameter (OD) is the same as the nominal size.
To understand this concept, it’s important to learn how pipes are manufactured.
For NPS sizes ranging from ⅛ inch (DN 6) to 12 inches (DN 300), the manufacturing process is based on a fixed outside diameter. As the wall thickness of the pipe increases, its inside diameter (ID) decreases. Therefore, the nominal pipe size falls somewhere between the outside diameter and the inside diameter.
For NPS 14 and larger pipes, the outside diameter corresponds directly to the nominal size of the pipe. The example below provides a clearer understanding of the concept.
| OD in Inch | OD in mm | Thickness in Inch | Thickness in mm | ID in Inch | ID in mm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| For NPS 2 Schedule 40 pipe | |||||
| 2.375 | 60.3 | 0.154 | 3.91 | 2.067 | 52.5 |
| For NPS 14 Schedule 40 pipe | |||||
| 14 | 350 | 0.438 | 11.13 | 13.124 | 333.3 |
From the table above, you can observe that for NPS 2, the Pipe ID is close to the NPS, while for NPS 14, the pipe OD matches the NPS.
What is Pipe NB (Nominal Bore)?
NPS is often referred to as NB (Nominal Bore), and there is no difference between the two terms. NB is commonly used in the United States to describe pipe dimensions. Additionally, when pipe sizes are expressed in millimeters (DN), people may also refer to these sizes in terms of NB. Therefore, when someone mentions a 25 NB pipe or a 50 NB pipe, they are essentially talking about DN.
What is DN (Diameter Nominal) Pipe Size?
DN, or Diameter Nominal, is an international designation (SI or Metric Designator) and serves as the European equivalent of NPS for indicating pipe sizes. It’s important to note that DN represents pipe sizes differently than NPS. For example, a 2-inch pipe is designated as DN 50. To convert NPS to DN, you can multiply the NPS value by 25. See the table below for easy reference. Keep in mind that there are no changes in other dimensions when using DN.
Pipe Size Conversion Chart
| NPS (inches) | DN (mm) | NPS (inches) | DN (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1/8 | 6 | 20 | 500 |
| 1/4 | 8 | 22 | 550 |
| 3/8 | 10 | 24 | 600 |
| 1/2 | 15 | 26 | 650 |
| 3/4 | 20 | 28 | 700 |
| 1 | 25 | 30 | 750 |
| 1 ¼ | 32 | 32 | 800 |
| 1 ½ | 40 | 36 | 900 |
| 2 | 50 | 40 | 1000 |
| 2 ½ | 65 | 42 | 1050 |
| 3 | 80 | 44 | 1100 |
| 3 ½ | 90 | 48 | 1200 |
| 4 | 100 | 52 | 1300 |
| 5 | 125 | 56 | 1400 |
| 6 | 150 | 60 | 1500 |
| 8 | 200 | 64 | 1600 |
| 10 | 250 | 68 | 1700 |
| 12 | 300 | 72 | 1800 |
| 14 | 350 | 76 | 1900 |
| 16 | 400 | 80 | 2000 |
| 18 | 450 | Based on ASME B36.10 | |
Initially, the pipe sizes increase by ¼ inch and then by ½ inch. From 6 inches to 42 inches, they increase by 2 inches, and afterwards, the increments are by 4 inches.
What is Pipe Schedule?
The pipe schedule refers to the method of specifying pipe wall thickness. To simplify the ordering of pipes, the ASME committee developed the Schedule Number, which is based on a modified version of Barlow’s formula for wall thickness.
Definition of Schedule Number:
The schedule number indicates an approximate value of the expression (1000 x P/S), where (P) represents the service pressure and (S) is the allowable stress, both measured in pounds per square inch (psi).
The formula for calculating the schedule number is as follows:
Schedule number = P/S
P is the service pressure in (psi)
S is the allowable stress in (psi)
What does Schedule 40 mean?
Schedule 40 is simply a designator for pipe thickness. In other words, for a given material, schedule 40 pipes can withstand a specific amount of pressure.
Which is thicker: Schedule 40 or Schedule 80 pipes?
Schedule 80 pipe is thicker than Schedule 40 pipe. According to the formula for the schedule number, since the allowable stress for a material at a given temperature is constant, an increase in service pressure will lead to a higher schedule number, indicating a thicker pipe wall.
Pipe Schedule for Stainless Steel Pipe
Stainless steel pipes are typically more expensive than carbon steel pipes. However, due to their corrosion-resistant properties, advancements in high-alloy stainless steel, and the use of fusion welding techniques, pipes with reduced wall thickness can operate effectively without the risk of premature failure.
To help mitigate material costs, the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) has introduced different schedule numbers for stainless steel pipes and fittings. Specifically, ASME B36.19 includes schedule numbers with an “S” suffix for stainless steel pipes (for example, 10S).
Standard Pipe Schedule as per ASME B36.10 and B36.19
Refer to the table below for a summary of available schedule numbers for carbon steel and stainless steel pipes, as per ASME B36.10 and B36.19.
| For Carbon Steel and Wrought iron Pipe as per ASME B36.10 | 5, 10, 20, 30, 40, 60, 80, 100, 120, 140, 160, STD, XS, XXS |
|---|---|
| For Stainless Steel Pipe as per ASME B36.19 | 5S, 10S, 40S, 80S |
Nominal Pipe Size OD
| Nominal Pipe Size in Inch | Nominal Pipe Size OD in Inch | DN in mm | Nominal Pipe Size OD in mm |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1/8 | 0.405 | 6 | 10.3 |
| 1/4 | 0.54 | 8 | 13.7 |
| 3/8 | 0.675 | 10 | 17.1 |
| 1/2 | 0.84 | 15 | 21.3 |
| 3/4 | 1.05 | 20 | 26.7 |
| 1 | 1.315 | 25 | 33.4 |
| 1.25 | 1.66 | 32 | 42.2 |
| 1.5 | 1.9 | 40 | 48.3 |
| 2 | 2.375 | 50 | 60.3 |
| 2.5 | 2.875 | 65 | 73 |
| 3 | 3.5 | 80 | 88.9 |
| 3.5 | 4 | 90 | 101.6 |
| 4 | 4.5 | 100 | 114.3 |
| 5 | 5.563 | 125 | 141.3 |
| 6 | 6.625 | 150 | 168.3 |
| 8 | 8.625 | 200 | 219.1 |
| 10 | 10.75 | 250 | 273.1 |
| 12 | 12.75 | 300 | 323.8 |
| 14 | 14 | 350 | 355.6 |
| 16 | 16 | 400 | 406.4 |
| 18 | 18 | 450 | 457 |
| 20 | 20 | 500 | 508 |
| 22 | 22 | 550 | 559 |
| 24 | 24 | 600 | 610 |
| 26 | 26 | 650 | 660 |
| 28 | 28 | 700 | 711 |
| 30 | 30 | 750 | 762 |
| 32 | 32 | 800 | 813 |
| 34 | 34 | 850 | 864 |
| 36 | 36 | 900 | 914 |
| 38 | 38 | 950 | 965 |
| 40 | 40 | 1000 | 1016 |
| 42 | 42 | 1050 | 1067 |
| 44 | 44 | 1100 | 1118 |
| 46 | 46 | 1150 | 1168 |
| 48 | 48 | 1200 | Nominal Pipe Size OD in inches |
Using the formula given below, you can calculate the Pipe Inside Diameter (ID) with the help of the Outside Diameter (OD) and the Thickness of the pipe.
Pipe ID = [Pipe O.D. – (2×Pipe wall thickness)]
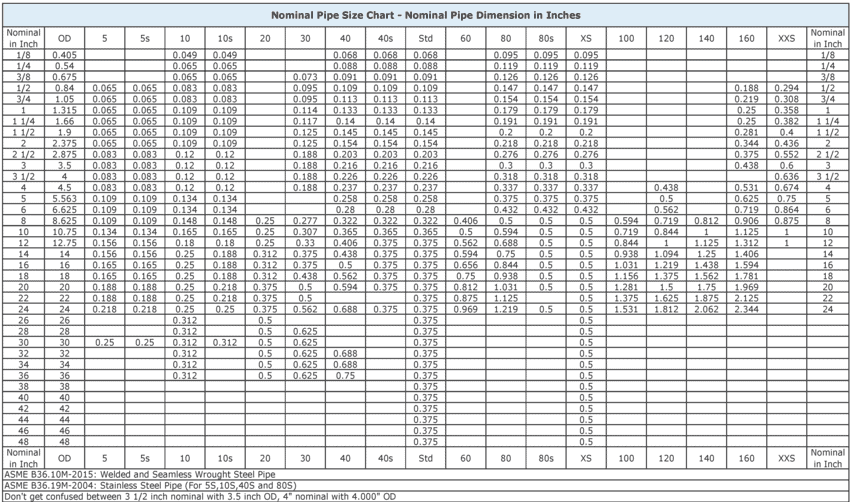
Pipe Size Chart in Inches:
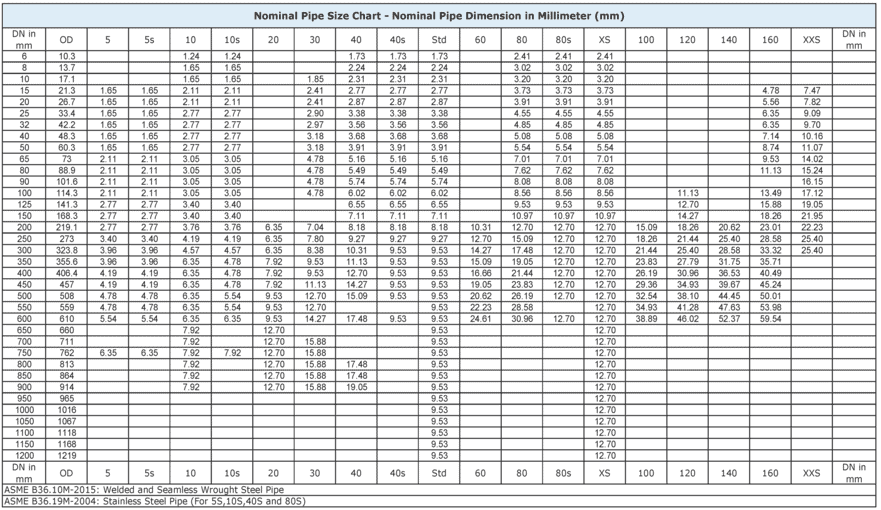
Pipe Size Chart in MM:
Pipe Size Chart in Inches & MM!
Pipe Size Chart in Inches!
Pipe Size Chart in MM!